Uttarakhand Innovations Explains Understanding the real estate definition is crucial for recognizing its value as an investment asset. Real estate encompasses land, buildings, and natural resources – making it a tangible and versatile investment option. It plays a significant role in wealth-building and financial planning, as it offers potential for long-term appreciation, steady rental income, and various tax benefits.
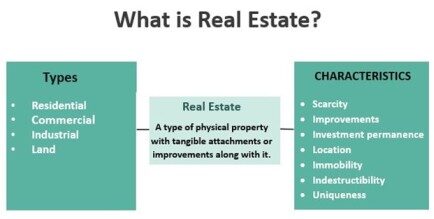
There are Generally four types of Real estate:-
- Residential – Properties where people live, such as houses, apartments, and condos.
- Commercial – Properties used for business purposes, like office buildings, shopping centers, and hotels.
- Industrial – Properties used for manufacturing or distribution, such as factories and warehouses.
- Land – Undeveloped property, agricultural land, or vacant plots of land.
Real estate is property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as growing crops, minerals or water, and wild animals; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this an item of real property, buildings or housing in general.
Main Key Aspects of Real Estate:-
- Real Estate Ownership
- Freehold Ownership: The owner has full rights to the property, including the land and buildings, and can sell, lease, or modify it as they see fit.
- Leasehold Ownership: This refers to a property that is leased for a certain number of years, decades, or even centuries, after which ownership reverts back to the landlord or property owner.
- Real Estate Transactions
- Buying and Selling: Involves transferring ownership of real property from one person to another, typically through a contract and closing process.
- Leasing and Renting: Renting is when a person (tenant) pays to occupy a property for a specific period, while leasing usually involves longer-term agreements. Lease agreements define the rights and responsibilities of both the tenant and landlord.
- Real Estate Market
- The real estate market can be influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Supply and Demand: More properties available for sale can lower prices, while fewer properties lead to higher prices.
- Interest Rates: When interest rates are low, it can be easier for buyers to afford homes, increasing demand.
- Location: A property’s location is often one of the most significant factors in determining its value.
- The real estate market can be influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Real Estate Investment
- Real estate is a popular investment vehicle because it can provide passive income and appreciate in value over time. Some common forms of real estate investment include:
- Residential Properties: Renting out single-family homes or multi-family units.
- Commercial Properties: Owning office buildings, retail spaces, or industrial properties.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate. REITs allow individuals to invest in real estate without directly owning properties.
- Vacation Rentals: Short-term rental properties, often through platforms like Airbnb.
- Real estate is a popular investment vehicle because it can provide passive income and appreciate in value over time. Some common forms of real estate investment include:
- Real Estate Development
- Development involves purchasing land or properties to improve them, often with the intention of selling or leasing at a profit. This can include building new homes, commercial buildings, or renovating existing structures.
- Urbanization and Zoning Laws: Developers must also consider zoning laws and regulations that dictate how land can used (e.g., residential, commercial, industrial). These laws influence development projects and property values.
Factors Affecting Real Estate Prices:-
- Economic Conditions:-
- A strong economy with job growth can drive up demand for housing and commercial space, increasing property values.
- Economic downturns can lead to lower demand, causing prices to decrease.
- Government Policies:-
- Tax policies, interest rates, and housing subsidies can impact the real estate market. For example, a government that offers first-time homebuyer incentives might stimulate more buying activity.
- Social Factors:-
- Changes in demographics (such as aging populations or migration trends) can influence demand for certain types of real estate. For example, cities may see a growing need for senior living communities, or young professionals may drive up demand for urban apartments.
- Technological Developments:-
- The rise of technologies like virtual tours, online real estate platforms, and smart home features have changed how people buy, sell, and use real estate.
- Environmental Factors:-
- Natural disasters or environmental risks (like flooding or earthquakes) can negatively impact real estate markets in certain areas. Buyers and investors tend to avoid properties located in high-risk zones.
Real Estate Terminology:-
- Natural disasters or environmental risks (like flooding or earthquakes) can negatively impact real estate markets in certain areas. Buyers and investors tend to avoid properties located in high-risk zones.
- Appraisal:- An assessment of a property’s value, usually conducted by a certified professional appraiser.
- Closing Costs:-Fees and expenses paid at the end of a real estate transaction, such as title insurance, property taxes, and broker fees.
- Mortgage:- A loan used to purchase real estate, where the property itself serves as collateral.
- Escrow:- A neutral third party holds funds or property until certain conditions are met during a transaction.
- Equity:- The difference between the current value of a property and the amount owed on any mortgages or liens against it.
- Title:- Legal ownership of a property. A “clear title” means the property is free from any legal encumbrances.
Real Estate Careers:-

- Real Estate Agent/Broker: These professionals help clients buy, sell, or rent properties. Brokers typically have more experience or training than agents and can operate their own real estate firms.
- Real Estate Developer: These individuals are responsible for acquiring land, securing financing, and managing construction projects to develop new properties.
- Real Estate Investor: Investors buy properties to generate rental income or sell them at a profit.
- Property Manager: A property manager oversees the day-to-day operations of a rental property, handling tasks such as tenant relations, repairs, and rent collection.
- Appraiser: A real estate appraiser determines the value of a property, typically when it is being bought, sold, or refinanced.
Current Trends in Real Estate:-
- Sustainability and Green Building: As awareness of climate change grows, the demand for eco-friendly homes and buildings is on the rise. Real estate developers and buyers are looking for energy-efficient, sustainable properties with features like solar panels, efficient insulation, and eco-friendly materials.
- Smart Homes: Technology is transforming how people interact with their homes. Smart home features like thermostats, lights, and security systems that can be controlled remotely are becoming increasingly common in residential real estate.
- Work-from-Home Impact: The rise of remote work, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has affected real estate trends. Many people are moving away from urban areas to suburban or rural locations for more space, better quality of life, and lower costs.
- Affordable Housing: In many parts of the world, the demand for affordable housing is rising. Governments and developers are exploring creative solutions to address housing shortages and affordability issues.
Uttarakhand innovations Explains all Real estate is a dynamic and multifaceted industry, and staying informed about market trends and opportunities is essential for anyone looking to engage in buying, selling, or investing in property. Real estate encompasses the land, plus any permanent man-made additions, such as houses and other buildings. Any additions or changes to the land that affects the property’s value are called an improvement.